We spend a good amount of time selecting the perfect frames for our eye glasses. However, most of us know and understand very little about the lenses. The lenses are the most important part of our eye glasses. The lenses that you choose are based mainly on your prescription. Therefore, we should spend some time trying to understand the lenses.
In the past, lenses were mainly made of glass. Presently, new materials and technology advances have enabled the eye care industry to provide a variety of lenses, apart from glass lenses. The following is a guide to help you understand the different types of lenses and lens coatings to consider the next time you buy a pair of glasses.
- Single Vision Lens
Single vision lenses are the most commonly prescribed lenses. The entire lens is dedicated to resolving a vision problem such as myopia, hyperopia or astigmatism.
- Aspheric Lenses
Aspheric lenses have a slimmer, lighter and more appealing profile compared to conventional lenses. In comparison to conventional lenses, aspheric lenses correct the distortion that occurs as your eye moves from the centre of the glasses toward the edges. This is attributed to the lenses’ complex front surface whose curvature thins toward the edge of the lens. The curvature allows aspheric lenses to be made with much flatter curves reducing the bulging of the lens from the frame. The lenses allow you to select a large array of frames without worry that the lens edge is too thick.
- Photo-chromic lenses
Photo-chromic lenses are lenses that darken on exposure to the sun (UV rays). Eye glasses with photo-chromic lenses are clear indoors but automatically activate the tint when out in the sun. With photo-chromic lenses you do not need to purchase a separate pair of sunglasses.
- Multi-focal eyeglass
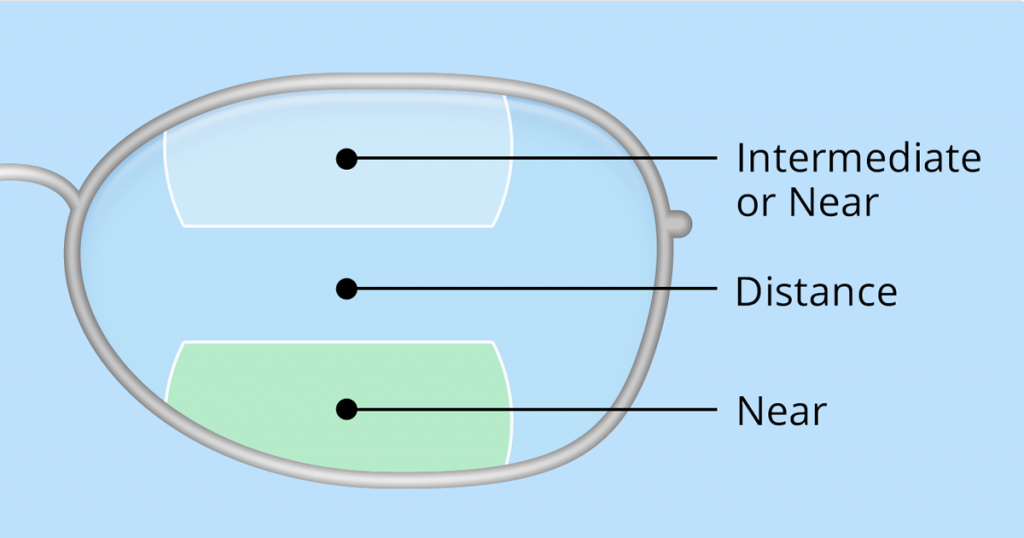
Multi-focal eye glasses have two or three lens powers. Multi-focal eye glasses are mostly prescribed to compensate for presbyopia. Presbyopia is a vision problem that occurs with age due to the eyes reduced ability to focus on near objects.
- Bifocals: consist of two viewing areas. They may be subdivided into a lower section and an upper section. The larger upper section helps you with focusing on long distances while the smaller lower part helps you focus on closer distances, as well as, reading.
- Progressive lenses (close up, Middle Distance, Far Distance) : include third lens power that allows the user to better focus on objects in close proximity, such as, the computer screen. Progressive lenses provide the user with the lens power of multi-focal However, progressive lenses also have other advantages including
- Your vision will be clear at all distances as opposed to two levels of distance provided by bifocals
- Secondly, the lenses have no visible line partitions between the different viewing areas. Hence, they provide a better aesthetic look.
- Polarized Lenses
Polarized lenses filter the light that enters your eye, and improves your vision and safety in the sun. Too much light can be blinding especially if you are engaging in activities out in the sun. Polarized lenses help you deal with the sun’s glare by blocking out and bouncing off any excessive light.